How Mars is losing its atmosphere faster than Earth.
By Ishank Katyal

According to the study and data of images sent by Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) of ISRO and NASA’s Mars orbiter and Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (Maven), the planet is losing its atmosphere to outer space at a faster rate as compared to that of Earth due to global dust storms.
Mars is being relatively smaller planet than Earth is losing its atmosphere at a faster rate than Earth, says the report of The Times of India.
Now the question comes that how Mars is losing its atmosphere to outer space? Well many other terrestrial planets in the Solar system are also constantly losing their atmospheres to outer space. The rate of losing depends on the size of the planet and the temperature of its upper atmosphere. Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) posted some findings on Wednesday on its website which are the studies of scientists who have studied data and images sent by MOM and Maven about the dust storms happened in the Red Planet on June- July 2018. This global storm was one of the biggest meteorological phenomena on Mars.
ISRO’s study on dust storms on Mars
The statement by ISRO said, “In the first week of June 2018, a global dust storm, also called a “planet- encircling dust event”, started growing in Mars and it had grown to its mature phase by the first week of July. Such a storm significantly heated and expanded the Martian upper atmosphere. The heating and expansion of the global dust storm led to a part of Mars atmosphere quickly reach the exobase altitude (which lies at 220 km). any hot gases above the exobase altitude are more likely to move to further higher altitudes and subsequently escape to outer space. Hence, from the results of the present study it can be inferred that the 2018 global dust storm resulted in enhanced escape of the Martian atmosphere.”
MOM also discovered that the evening side of the Mars is going down to altitude as low as 155 km. The Mars Exospheric Neutral Composition Analyser (MENCA) instrument, a mass spectrometer onboard the ISRO orbiter, measured the neutral densities of the planet’s thermosphere (which lies between 100 and 200 km). Any hot gases above the exobase altitude are more likely to move to further higher altitudes and subsequently escape to outer space. Hence, from the results of the present study it can be inferred that the 2018 global dust storm resulted in enhanced escape of the Martian atmosphere.”
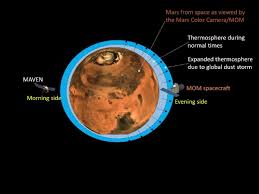
MOM also discovered that the evening side of the Mars is going down to altitude as low as 155 km. The Mars Exospheric Neutral Composition Analyser (MENCA) instrument, a mass spectrometer onboard the ISRO orbiter, measured the neutral densities of the planet’s thermosphere (which lies between 100 and 200 km).
After analysing these measurements, scientists at the National Atmospheric Research Laboratory, Gadanki, Andhra Pradesh, found that the upper atmosphere of the Mars is going to warm and expand.
